Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Optics and Photonics, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081, P. R. China
2 School of Medical Technology, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081, P. R. China
3 Department of Laser Medicine, First Medical Center of PLA General Hospital, Beijing 100853, P. R. China
4 Britton Chance Center for Biomedical Photonics – MoE Key Laboratory for Biomedical Photonics, Advanced Biomedical Imaging Facility, Wuhan National Laboratory for Optoelectronics, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430074, Hubei, P. R. China
5 Precision Laser Medical Diagnosis and Treatment Innovation Unit, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Beijing 100000, P. R. China
Vascular-targeted photodynamic therapy (V-PDT) is an effective treatment for port wine stains (PWS). However, repeated treatment is usually needed to achieve optimal treatment outcomes, possibly due to the limited treatment light penetration depth in the PWS lesion. The optical clearing technique can increase light penetration in depth by reducing light scattering. This study aimed to investigate the V-PDT in combination with an optical clearing agent (OCA) for the therapeutic enhancement of V-PDT in the rodent skinfold window chamber model. Vascular responses were closely monitored with laser speckle contrast imaging (LSCI), optical coherence tomography angiography, and stereo microscope before, during, and after the treatment. We further quantitatively demonstrated the effects of V-PDT in combination with OCA on the blood flow and blood vessel size of skin microvasculature. The combination of OCA and V-PDT resulted in significant vascular damage, including vasoconstriction and the reduction of blood flow. Our results indicate the promising potential of OCA for enhancing V-PDT for treating vascular-related diseases, including PWS.
Vascular-targeted photodynamic therapy (V-PDT) optical clearing agent (OCA) treatment efficacy enhancement skin-fold window chamber port wine stains Journal of Innovative Optical Health Sciences
2024, 17(2): 2350023
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Medicine, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300072, P. R. China
2 Department of Laser Medicine. The First Medical Center of Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing 100853, P. R. China
3 Department of Oncology, The Seventh Medical Center of Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing 100039, P. R. China
4 School of Basic Medicine, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550025, Guizhou, P. R. China
5 College of Medical Technology, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081, P. R. China
6 Medical School of Chinese PLA, Beijing 100853, P. R. China
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) has limited effects in treating metastatic breast cancer. Immune checkpoints can deplete the function of immune cells; however, the expression of immune checkpoints after PDT is unclear. This study investigates whether the limited efficacy of PDT is due to upregulated immune checkpoints and tries to combine the PDT and immune checkpoint inhibitor to observe the efficacy. A metastatic breast cancer model was treated by PDT mediated by hematoporphyrin derivatives (HpD-PDT). The anti-tumor effect of HpD-PDT was observed, as well as CD4T, CD8T and calreticulin (CRT) by immunohistochemistry and immunofluorescence. Immune checkpoints on T cells were analyzed by flow cytometry after HpD-PDT. When combining PDT with immune checkpoint inhibitors, the antitumor effect and immune effect were assessed. For HpD-PDT at 100mW/cm2 and 40, 60 and 80J/cm2, primary tumors were suppressed and CD4T, CD8T and CRT were elevated; however, distant tumors couldn’t be inhibited and survival could not be prolonged. Immune checkpoints on T cells, especially PD1 and LAG-3 after HpD-PDT, were upregulated, which may explain the reason for the limited HpD-PDT effect. After PDT combined with anti-PD1 antibody, but not with anti-LAG-3 antibody, both the primary and distant tumors were significantly inhibited and the survival time was prolonged, additionally, CD4T, CD8T, IFN-CD4T and TNF-CD4T cells were significantly increased compared with HpD-PDT. HpD-PDT could not combat metastatic breast cancer. PD1 and LAG-3 were upregulated after HpD-PDT. Anti-PD1 antibody, but not anti-LAG-3 antibody, could augment the antitumor effect of HpD-PDT for treating metastatic breast cancer.
Photodynamic therapy anti-PD1 antibody anti-LAG-3 antibody anti-tumor immune effects metastatic breast cancer Journal of Innovative Optical Health Sciences
2024, 17(1): 2350020
1 北京航空航天大学生物与医学工程学院北京市生物医学工程高精尖创新中心,北京 100083
2 解放军总医院第一医学中心激光医学科,北京 100853
换能器作为超声系统的核心部分,起着重要的作用。传统的超声换能器是电驱动器件,利用材料的压电效应实现电-声转换,然而面对应用环境的苛刻要求,其有限的带宽限制了其在高标准要求环境中的应用。光致超声作为一种新型技术,利用激光代替电作为激励源获得超声,拥有传统压电技术无法具备的特性,如高频率和大带宽,这是成像和传感所需要的。同时,光致超声技术具有较为简单的换能器构架,避免了电子元件组装的复杂性,使得各种形状的超声换能器开发成为可能,比如凹形换能器和全向换能器。光致超声技术的这些优势使其有望获得更广泛的应用。对光致超声技术进行了介绍,主要包括光声机制、换能器性能表征和该技术在生物医学领域中的最新应用,并进一步讨论了光致超声技术未来可能的发展方向。
生物光学 光声效应 超声波 光致超声换能器 高频超声 中国激光
2023, 50(21): 2107105
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory for Mesoscopic Physics, Department of Physics, Peking University, Beijing 100871, China
2 Frontiers Science Center for Nano-optoelectronics & Collaborative Innovation Center of Quantum Matter & Beijing Academy of Quantum Information Sciences, Peking University, Beijing 100871, China
3 Collaborative Innovation Center of Extreme Optics, Shanxi University, Taiyuan 030006, China
4 Peking University Yangtze Delta Institute of Optoelectronics, Nantong 226010, China
5 Hefei National Laboratory, Hefei 230088, China
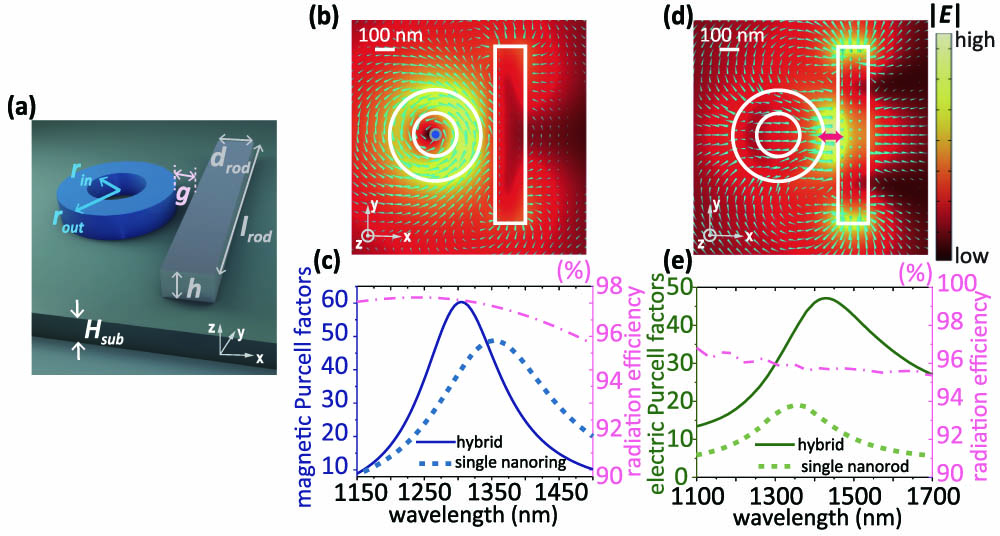
Hybrid metal-dielectric structures combine the advantages of both metal and dielectric materials, enabling high-confined but low-loss magnetic and electric resonances through deliberate arrangements. However, their potential for enhancing magnetic emission has yet to be fully explored. Here, we study the magnetic and electric Purcell enhancement supported by a hybrid structure composed of a dielectric nanoring and a silver nanorod. This structure enables low Ohmic loss and highly-confined field under the mode hybridization of magnetic resonances on a nanoring and electric resonances on a nanorod in the optical communication band. Thus, the 60-fold magnetic Purcell enhancement and 45-fold electric Purcell enhancement can be achieved. Over 90% of the radiation can be transmitted to the far field. For the sufficiently large Purcell enhancement, the position of emitter has a tolerance of several tens of nanometers, which brings convenience to experimental fabrications. Moreover, an array formed by this hybrid nanostructure can further enhance the magnetic Purcell factors. The system provides a feasible option to selectively excite magnetic and electric emission in integrated photonic circuits. It may also facilitate brighter magnetic emission sources and light-emitting metasurfaces with a more straightforward design.
Purcell effect magnetic emission hybrid structures Chinese Optics Letters
2023, 21(10): 103602
1 北京理工大学光电学院,北京 100081
2 北京市混合现实与新型显示工程技术研究中心,北京 100081
3 北京理工大学计算机学院,北京 100081
4 北京理工大学医学技术学院,北京 100081
5 中国人民解放军总医院激光医学科,北京 100853
手术导航综合运用器官分割建模与手术规划、位姿标定与跟踪定位、多模态图像配准与融合显示等技术,使医生精确定位病灶与手术工具的位置,透过组织表面对内部组织进行观测,可大幅提升手术的安全性,缩短手术时间并提高手术效率。常规手术通常使用超声、内窥镜或X光等单模态影像进行手术过程引导,信息单一且均为二维影像,空间立体信息缺失,手术过程严重依赖医生经验;而多模态图像引导的手术导航技术通过融合多模态图像的优势,在三维空间提供病灶的结构或功能信息,大幅提升医生对血管、神经以及重要组织结构的空间辨识力。由此,本文针对多模态图像分割建模、手术方案决策、手术空间位姿标定与跟踪、多模态图像配准、图像融合与显示等多模态图像引导手术导航的关键技术进行总结和分析,提出其进一步发展面临的挑战并展望其未来发展趋势。多模态图像引导手术导航技术已成为神经外科、颅颌面、骨科、经皮穿刺、血管介入等临床科室精准治疗的新兴手段,具有重要的应用前景。
手术导航 手术机器人 多模态医学影像 医学图像处理 定位跟踪 配准融合 光学学报
2023, 43(15): 1500002

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Chinese PLA General Hospital, the First Medical Center, Department of Laser Medicine, Beijing, China
2 Hainan Hospital, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Laser Medicine Center, Sanya, China
A phase-only method is proposed to transform an optical vortex field into desired spiral diffraction–interference patterns. Double-ring phase apertures are designed to produce a concentric high-order vortex beam and a zeroth-order vortex beam, and the diffracted intensity ratio of two beams is adjustable between 0 and 1. The coherent superposition of the two diffracted beams generates a brighter Airy spot (or Poisson spot) in the middle of the spiral pattern, where the singularity for typical vortex beam is located. Experiments employing circular, triangular, and rectangular phase apertures with topological charges from 3 to 16 demonstrate a stable, compact, and flexible apparatus for vortex beam conversion. By adjusting the parameters of the phase aperture, the proposed method can realize the optical Gaussian tweezer function and the optical vortex tweezer function simultaneously along the same axis or switch the experimental setup between the two functions. It also has potential applications in light communication through turbulent air by transmitting an orbital angular momentum-coded signal with a concentric beacon laser.
finite aperture diffraction phase-only beam transformation orbital angular momentum common-path interferometry optical manipulation light transmission through turbulent air Advanced Photonics Nexus
2023, 2(3): 036008
1 北京理工大学光电学院,北京 100081
2 清华大学附属北京清华长庚医院血管外科,清华大学临床医学院,北京 102218
3 清华大学精密仪器系激光与光子技术研究室,光子测控技术教育部重点实验室,北京 100084
4 中国人民解放军总医院第一医学中心激光医学科,北京 100853
脉冲串飞秒激光在工业精密加工中展现出低热高效的特性,有望为血栓清除技术提供新型解决方案。以动物血凝块为消蚀样本,将脉冲串飞秒激光与高速振镜相结合来搭建实验平台,对样本表面进行单层扫描消蚀,使用三维超景深显微镜对消蚀坑进行观察和记录,并与相同平均功率下的传统脉冲模式飞秒激光的消蚀结果进行比较。结果表明,相比于传统脉冲模式,脉冲串飞秒激光可以提升消蚀效率并降低消蚀阈值,具有良好的临床研发潜力。
医用光学 飞秒激光 组织消蚀 脉冲串模式 三维显微成像
1 北京理工大学医学技术学院,北京 100081
2 解放军总医院第一医学中心激光医学科,北京 100853
光动力疗法(PDT)是一种通过光动力反应选择性地治疗恶性肿瘤及癌前病变等疾病的新型疗法,具有广阔的临床应用前景。光敏剂作为PDT的关键要素之一,其在体浓度分布直接影响PDT疗效,实现光敏剂剂量在体定量检测是开展个性化PDT精准治疗的前提。介绍了光敏剂浓度在体定量检测的影响因素;总结了目前常用的光敏剂荧光光谱定量校准方法及荧光定量检测技术;最后讨论了光敏剂定量检测技术在PDT临床转化应用中所面临的挑战和发展方向。
医用光学 光敏剂 光动力疗法 剂量 定量检测 荧光 临床应用
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Medicine, Nankai University, Tianjin 300072, P. R. China
2 Department of Laser Medicine, The First Medical Center of Chinese PLA, General Hospital Beijing 100853, P. R. China
3 College of Medical Technology, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081, P. R. China
4 Department of Oncology, The Seventh Medical Center of Chinese PLA, General Hospital Beijing 100039, P. R. China
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) not only destroys tumor cells directly but also induced anti-tumor immune response through damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs). It is reported that anti-tumor response was associated with light dose and photosensitizer used in PDT. In this study, 4T1 tumor cells were implanted on both the right and left flanks of mice. Only the right tumor was treated by HpD-PDT, while the left tumor was not irradiated. The anti-tumor immune response induced by HpD-PDT was investigated. The expression of DAMPs and costimulatory molecules induced by HpD-PDT were tested by immunofluorescence and flow cytometry in vivo. Different light doses of PDT were designed to treat 4T1 cells. The killing effect was assessed by CCK-8 kit and apoptosis kit. The expression of DAMPs on 4T1 cells after HpDPDT were evaluated by flow cytometry, western blot and ATP kit. This study showed that CD4tT, CD8tT and the production of IFN-γ were increased significantly on day 10 in righttumor after PDT treatment compared with control group. HpD-PDT enhanced the expression of calreticulin (CRT) on tumor tissue. Importantly, co-stimulatory molecular OX-40 and 4-1BB were elevated on CD8tT cells. In vitro, immunogenic death of 4T1 cells was induced after PDT. Besides, the expression of DAMPs increased with the increasing of energy density. This study indicates that anti-tumor immune effect was induced by HpD-PDT. The knowledge of the involvement of CRT, ATP and co-stimulatory molecules uncovers important mechanistic insight into the anti-tumor immunogenicity. It was the first time that co-stimulatory molecules were investigated and found to elevate after PDT.
Photodynamic therapy hematoporphyrin derivatives anti-tumor immune effect immunogenic cell death costimulatory molecule Journal of Innovative Optical Health Sciences
2022, 15(4): 2240002
1 解放军医学院,北京 100853
2 解放军总医院第一医学中心激光医学科,北京 100853
3 北京理工大学医学技术学院,北京 100081
4 中国医学科学院精准激光诊疗创新单元,北京 100730
鲜红斑痣(port wine stains, PWS)是最常见的先天性皮肤微血管病变之一,PWS的病因是皮肤真皮层由浅至深的毛细血管畸形扩张。通常表现为面颈部粉色、红色和紫色斑片,随着年龄的增加,其逐渐加深和增厚,严重影响患者的生活质量。血管靶向光动力疗法 (vascular targeted photodynamic therapy, V-PDT) 可以选择性破坏病变血管,是目前国内治疗PWS的首选方法。V-PDT疗效与PWS病灶结构密切相关。PWS的病灶结构可通过活检或者无创光学诊断设备获取,主要包括表皮层黑色素含量、皮肤厚度及血管管径、深度和形态等。总结了目前常用的无创在体光学成像技术在PWS诊疗中的应用现状及PWS病灶结构特点对V-PDT疗效的影响,旨在为V-PDT精准及个性化治疗PWS提供参考。
医用光学 鲜红斑痣 血管靶向光动力疗法 病灶结构 疗效 中国激光
2022, 49(15): 1507102





